Discover the passion and craftsmanship behind CRŪ Winery's award-winning wines. From the cool coastal vineyards of the Central Coast to their dedicated winemaking team, this story uncorks the rich flavors and exclusive experiences that make CRŪ a standout in the wine world. (GV Wire/Dean Kirkland)

- Madera’s climate creates diverse, robust wines, — unique from Napa's more famous offerings.
- CRŪ and other Madera wineries offer personal, tradition-rich experiences, enhancing each visit.
- CRŪ features serene coastal tastings in Monterey and intimate, behind-the-scenes tours in Madera.
Share
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Madera’s wine scene is like a well-kept secret — it’s not as flashy as Napa or Sonoma, but it’s got a charm all its own.

Dean Kirkland
The Wines of Fresno
Madera offers a unique environment that lends itself to a variety of grape varieties. The region’s warm climate and rich soils make it ideal for growing robust reds and crisp whites.
As Rebecca Gilbert, the Senior Director of Marketing and Communications at CRŪ Winery, puts it, “Madera may not be the first place people think of for wine, but it’s a region where tradition meets innovation, and the wines are as diverse as the people who make them.”
One of the standout features of Madera wineries is their emphasis on family-owned operations. Many of these wineries have been passed down through generations, with winemaking techniques honed over the years like a finely tuned engine. The sense of community here is palpable; it’s not uncommon to find the winemaker pouring your tasting flight or the vineyard owner tending the vines.
“It’s this personal touch that sets Madera apart and makes each visit a unique experience,” says Tamara Rutten, the Tasting Room Manager at CRŪ.

CRŪ Winery began with a love for the Madera area and a desire to share their wines with the local community. “Our founders are from this area, and they wanted to create a winery within the Madera and Fresno area to share the wines they were producing from throughout California with their friends,” Rebecca explains.
CRŪ Winery
20146 Rd. 21, Madera, CA 93637
Open Daily, 11 a.m.-5 p.m.
Phone: (559) 673-6372
Reservations: exploretock.com
Website: cruwinery.com
This passion has grown into a well-respected winery with a wide distribution, sharing the distinct flavors of the Central Coast across the state, the country, and even a few international markets. Despite their growth, CRŪ remains grounded in its roots, focusing on the Central Coast and working with vineyards and growers from the Santa Cruz Mountains to the Santa Maria Valley to craft their wines. This dedication to quality and community is a hallmark of the Madera wine experience.
The Art of Wine Tasting: More Than Just a Swirl and Spit
Let’s get one thing straight: wine tasting isn’t just about getting a buzz while pretending to know what tannins are. It’s a nuanced experience that engages all your senses. Here’s a quick rundown on how to taste wine like a pro:
-
Sight:
Before you even take a sip, take a good look at the wine. The color can tell you a lot about what you’re about to taste. For instance, a deep, inky red might suggest a full-bodied wine, while a pale straw color could indicate a light and crisp white. Melissa Smith, the Production Manager and Cellar Master at CRŪ, advises, “Tilt your glass at a 45-degree angle and hold it against a white background to get the best view. Look at the hue and clarity, and note any sediment.”
-
Smell:
Stick your nose in the glass and take a deep whiff. The aroma, or “nose,” is where you’ll catch the wine’s bouquet. Swirl the wine to aerate it and release its volatile compounds, which helps intensify the aromas. Close your eyes and imagine walking through a produce aisle—fruits, flowers, and spices are all fair game here. At CRŪ, for example, you might pick up notes of citrus, green tea, or even toasted marshmallow, depending on the wine.

Melissa Smith (left) and Rebecca Gilbert (right) enjoy a toast at CRŪ Winery. (GV Wire/Dean Kirkland) -
Taste:
Now for the fun part. Take a small sip and let the wine coat your palate. Pay attention to the flavors and how they evolve. Are you tasting ripe berries, a hint of oak, or maybe even a touch of minerality? The taste can also tell you about the wine’s structure—its acidity, tannins, and body. A well-balanced wine will have all these elements in harmony, like a perfectly tuned orchestra.
-
Touch (Mouthfeel):
This is where you consider the wine’s texture. Is it silky, gritty, or somewhere in between? The mouthfeel can give you clues about the wine’s age and how it was made. For instance, a creamy mouthfeel might indicate a wine that underwent malolactic fermentation, a process that converts sharp malic acid into softer lactic acid, much like milk.
-
Finish:
Finally, consider the finish, or aftertaste. Does the flavor linger, or does it disappear quickly? A long, complex finish is often a sign of a high-quality wine.
The Technical Side: From Vineyard to Bottle
Making wine is like restoring a classic car; it requires precision, patience, and a little bit of love. At CRŪ Winery, they take their grapes from some of California’s most prestigious regions, including the Santa Lucia Highlands and Paso Robles. These grapes are then meticulously crafted into wine through a process that blends tradition with modern technology.
Related Story: Ziveli Winery Is a Toast to Croatia in California’s Heartland
The Vineyard
CRŪ sources grapes from various regions, each bringing its own unique characteristics to the table. The Santa Lucia Highlands, for example, benefit from a cool coastal influence, which results in wines with bright acidity and complex flavors. Meanwhile, Paso Robles offers a warmer climate and diverse soils, ideal for producing bold, full-bodied reds.
Harvesting and Sorting
Once the grapes reach optimal ripeness, they’re harvested — often in the cool, early morning hours to preserve their freshness. The grapes are then sorted to remove any that don’t make the cut. This meticulous selection process ensures that only the best fruit goes into the wine.
Fermentation
Next up is fermentation, where the grape juice is transformed into wine. Depending on the type of wine being made, CRŪ might use stainless steel tanks or oak barrels for fermentation. Stainless steel is often used for white wines to maintain their crisp, clean character, while oak barrels can add layers of complexity to reds.
Aging
Aging is where the magic happens. For red wines, CRŪ employs a mix of new and neutral oak barrels. New oak imparts flavors like vanilla, spice, and sometimes a hint of smokiness. Neutral oak, on the other hand, allows the wine to breathe and develop without overpowering its natural flavors. The aging process can last anywhere from a few months to several years, depending on the desired style.

Bottling
Once the wine has aged to perfection, it’s time for bottling. This process involves carefully transferring the wine from barrels or tanks into bottles, all while minimizing exposure to oxygen. The bottles are then sealed, labeled, and left to rest before they’re ready to hit the market.
CRŪ Winery: A Snapshot
CRŪ Winery might be based in Madera, but its influence extends far beyond the Central Valley. With a tasting room in Monterey and distribution across the country, CRŪ offers a range of wines that showcase the best of California’s Central Coast. Whether you’re into the bright, citrusy notes of their Chardonnay or the rich, berry-laden profile of their Pinot Noir, there’s something for everyone.
Their Monterey tasting room, located in the picturesque Santa Lucia Highlands, provides a cool coastal escape where visitors can enjoy tastings in a serene setting. Meanwhile, the Madera location offers a more intimate experience, complete with behind-the-scenes tours and exclusive tastings. As Tamara Rutten, the Tasting Room Manager, describes, “We love giving guests a closer look at our winemaking process. It’s like offering a VIP pass to a garage full of vintage cars—each bottle has a unique story, and every tasting is a journey through the terroir and craftsmanship that define our wines.”

Related Story: Discover Moravia Winery: Danish Heritage & Exceptional Wines in Fresno
The CRŪ Madera Wine Experience
Madera may not have the star power of Napa or the glitz of Sonoma, but it is rich in history, passion, and, most importantly, excellent wine. The region’s emphasis on family-owned wineries and a hands-on approach to winemaking creates a welcoming atmosphere where visitors can truly connect with the people behind the wines. From the technical aspects of winemaking to the simple pleasure of tasting, Madera offers an experience that is both educational and enjoyable.
At CRŪ, this experience is elevated by the knowledge and passion of the staff. Whether you’re chatting with Rebecca Gilbert about the winery’s origins and mission or getting technical insights from Melissa Smith in the cellar, there’s a sense of pride and dedication that permeates every aspect of the winery. This commitment to quality and community is a hallmark of CRŪ and a defining feature of the broader Madera wine scene.
Related Story: Grape Expectations: A Day with Ray Krause, the Wine Wizard of Madera County

So, the next time you’re planning a wine adventure, consider a detour to Madera. It’s a place where you can enjoy world-class wines without the pretension, and where every winery has a story worth hearing. And if you find yourself at CRŪ Winery, take your time, savor each sip, and maybe even chat with the winemaker. As Tamara Rutten suggests, “Every visit is an opportunity to discover something new and exciting, whether it’s a unique wine pairing or an insider tip on the best local vineyards.” Cheers to the journey and the hidden gems of Madera’s wine country!
About the Author
GV Wire Producer Dean Kirkland is the founder and director of Gas and Gears, an independent film production company that has produced numerous television series and feature films, including the award-winning documentary “Racing Through The Forest” (2014).
RELATED TOPICS:
Categories
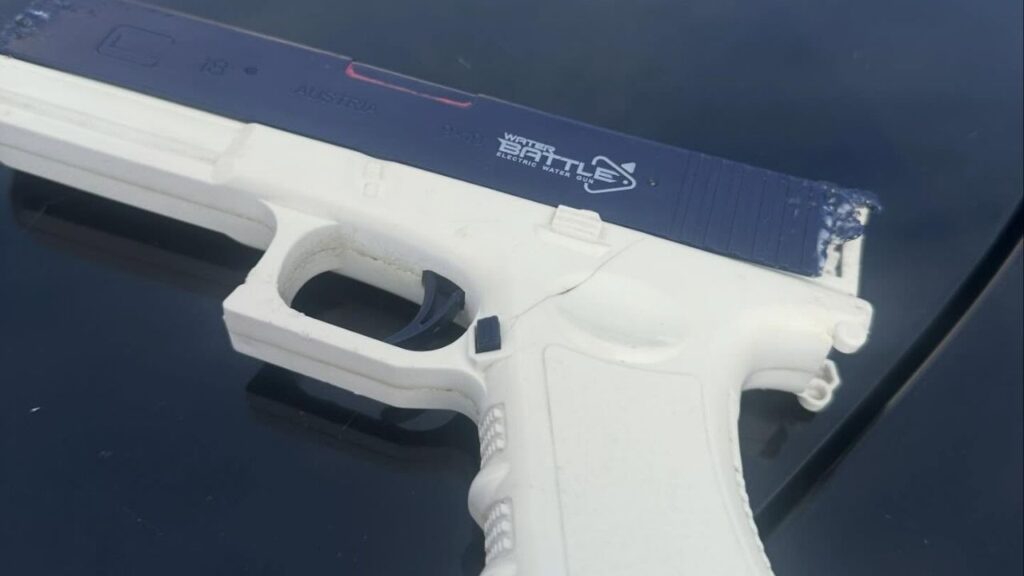

Teen Arrested at Visalia Mall After Firearm Report

Tumblr Goes Down for Thousands, Downdetector Reports