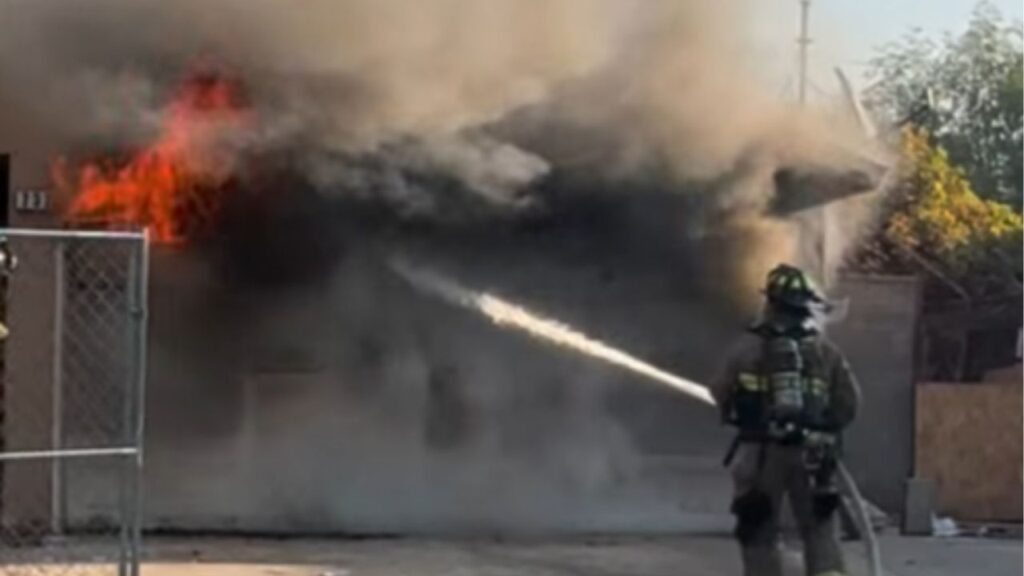
An illustration provided by Mark Garlick shows an artist’s impression of a large asteroid impacting Earth 66 million years ago, abruptly ending the age of dinosaurs. A new study adds strong evidence to the hypothesis that the deadly rock known as the Chicxulub impactor came from a family of objects that originally formed well beyond the orbit of the planet Jupiter. (Mark Garlick via The New York Times)

- The Chicxulub impactor was likely a rare carbonaceous asteroid, according to new ruthenium isotope evidence.
- The Chicxulub impactor is a unique case among 500-million-year-old impactors, differing from typical siliceous asteroids.
- The Chicxulub asteroid’s impact wiped out dinosaurs but paved the way for the rise of mammals, including humans.
Share
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Scientists have discovered new evidence that the rock that slammed into Earth 66 million years ago, abruptly ending the age of dinosaurs, was a bit of an oddball.
The Chicxulub Impactor
The nature of this apocalyptic object, known as the Chicxulub impactor, has inspired intense debates, including a long-running dispute over whether it was a comet or an asteroid. But evidence has been mounting in recent years that the roughly 6-mile-wide impactor belonged to a family of asteroids that formed beyond the orbit of Jupiter, and that rarely impact Earth.
Now, a team led by Mario Fischer-Gödde, a research scientist at the University of Cologne in Germany, has bolstered that case with the help of the rare element ruthenium. Ruthenium is abundant in asteroids but extremely scarce in Earth’s crust, making it a handy bellwether of past impacts by space rocks. The team searched for isotopes of ruthenium in the geological remnants of the Chicxulub impact.
Related Story: A Rarely Seen Deep Sea Fish Is Found in California, and Scientists Want to Know ...
The results revealed a uniform signature across the global layer of debris left by the impact, which is known as the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) boundary. And that signature neatly matches the makeup of a group of space rocks known as carbonaceous asteroids because of their high-carbon content, according to a study published in Science.
“It’s the nail in the coffin,” Fischer-Gödde said. “This ruthenium isotope signature that we measure cannot be anything else other than a carbonaceous asteroid.”
Previous studies have unearthed chemical signatures in the K-Pg boundary that also implicated a carbonaceous asteroid in the death of the nonavian dinosaurs and about two-thirds of all other species on Earth. But Fischer-Gödde and his colleagues have spent years focusing on ruthenium.
Ruthenium is so vanishingly absent on Earth that it takes only small amounts to associate it with an impact by a carbonaceous-type asteroid. “This is the beauty of the element ruthenium,” Fischer-Gödde said.
For a base line, Fischer-Gödde and his colleagues measured ruthenium in the samples of five other asteroid impacts that occurred over the past 541 million years. All of these impacts lined up with the composition of siliceous asteroids, a class that formed closer to the sun than carbonaceous asteroids and that are concentrated in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Most meteorites that end up on Earth’s surface are from this siliceous family.
“So far, Chicxulub, among the 500-million-year-old impactors, seems to be a unique and rare case of a carbonaceous-type asteroid hitting Earth,” Fischer-Gödde said.
Related Story: Reducing Children’s Screen Time to 3 Hours Weekly Works Wonders
Still Unclear How Asteroid Ended Up Hitting Earth
The siliceous asteroids that impact Earth usually come from the asteroid belt. But it is still unclear how a massive carbonaceous asteroid ended up on a collision course with our planet. One possible origin is a population of carbonaceous asteroids that exists today at the outer edge of the asteroid belt. Though these rocks initially formed beyond Jupiter, scientists think that gravitational instabilities in the early solar system launched them inward to their current position.
Previous research led by William Bottke, a senior planetary scientist at the Southwest Research Institute, has suggested that the deadly object could have been one of these carbonaceous asteroids from the asteroid belt.
Bottke said the new study was “useful” because it confirmed the likely back stories of several impacts on Earth and added “more detailed information to what was in the literature.”
David Kring, principal scientist at the Lunar and Planetary Institute of the Universities Space Research Association and an expert on the Chicxulub impact, said “the study is an outstanding application of a new analytical technique.”
Related Story: Stargazers Prepare for Peak of Perseid Meteor Shower This Weekend
“Identifying the type of impactor is important because it helps us evaluate the frequency of such impacts in the geologic past and the hazards of such impacts in the planet’s future,” Kring said.
Many mysteries remain about the Chicxulub impact, as well as about the broader role that asteroid strikes have played in the emergence and evolution of life on Earth — and, potentially, other planets. Carbonaceous asteroids have wiped out untold species in our planet’s past, but they may have also helped seed Earth with water, and other essential ingredients for life, at the dawn of the solar system.
And while the Chicxulub impactor doomed the dinosaurs, it simultaneously enabled the rise of mammals, including humans. So we may owe that rogue asteroid a measure of gratitude.
“Without this impact, what would our Earth look like today?” Fischer-Gödde said. “We should probably value, a bit more, that we are around and this is maybe a lucky coincidence that everything came to place like it is today.”
–
This article originally appeared in The New York Times.
By Becky Ferreira/Mark Garlick
c. 2024 The New York Times Company
RELATED TOPICS:
Categories

Trump Announces 10% Increase in Tariffs on Canada