Share
NEW YORK — One morning last fall, 4-year-old Joey Wilcox woke up with the left side of his face drooping.
It was the first sign of an unfolding nightmare.
“It’s devastating,” said his father, Jeremy Wilcox, of Herndon, Virginia. “Your healthy child can catch a cold — and then become paralyzed.”
Joey, who survived but still suffers some of the effects, was one of 228 confirmed victims in the U.S. last year of acute flaccid myelitis, or AFM, a rare, mysterious and sometimes deadly paralyzing illness that seems to ebb and flow on an every-other-year cycle and is beginning to alarm public health officials because it is striking more and more children.
Dr. Anthony Fauci, head of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said it may bear similarities to polio, which smoldered among humans for centuries before it exploded into fearsome epidemics in the 19th and 20th centuries.
‘Don’t Assume That It’s Going to Stay at a Couple of Hundred Cases Every Other Year’
Fauci, who published a report about the disease Tuesday in the journal mBio, said it is unlikely AFM will become as bad as polio, which struck tens of thousands of U.S. children annually before a vaccine became available in the 1950s.
But he warned: “Don’t assume that it’s going to stay at a couple of hundred cases every other year.”
While other countries have reported cases, including Canada, France, Britain and Norway, the size and pattern of the U.S. outbreaks have been more pronounced. More than 550 Americans have been struck this decade. The oldest was 32. More than 90% were children, most around 4, 5 or 6 years old.
Most had a cold-like illness and fever, seemed to get over it, then descended into paralysis. In some cases it started in small ways — for example, a thumb that suddenly wouldn’t move. Some went on to lose the ability to eat or draw breath.
Many families say their children have regained at least some movement in affected limbs, but stories of complete recovery are unusual. Health officials cannot say how many recovered completely, partly or not at all, or how many have died, though the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says deaths are rare.
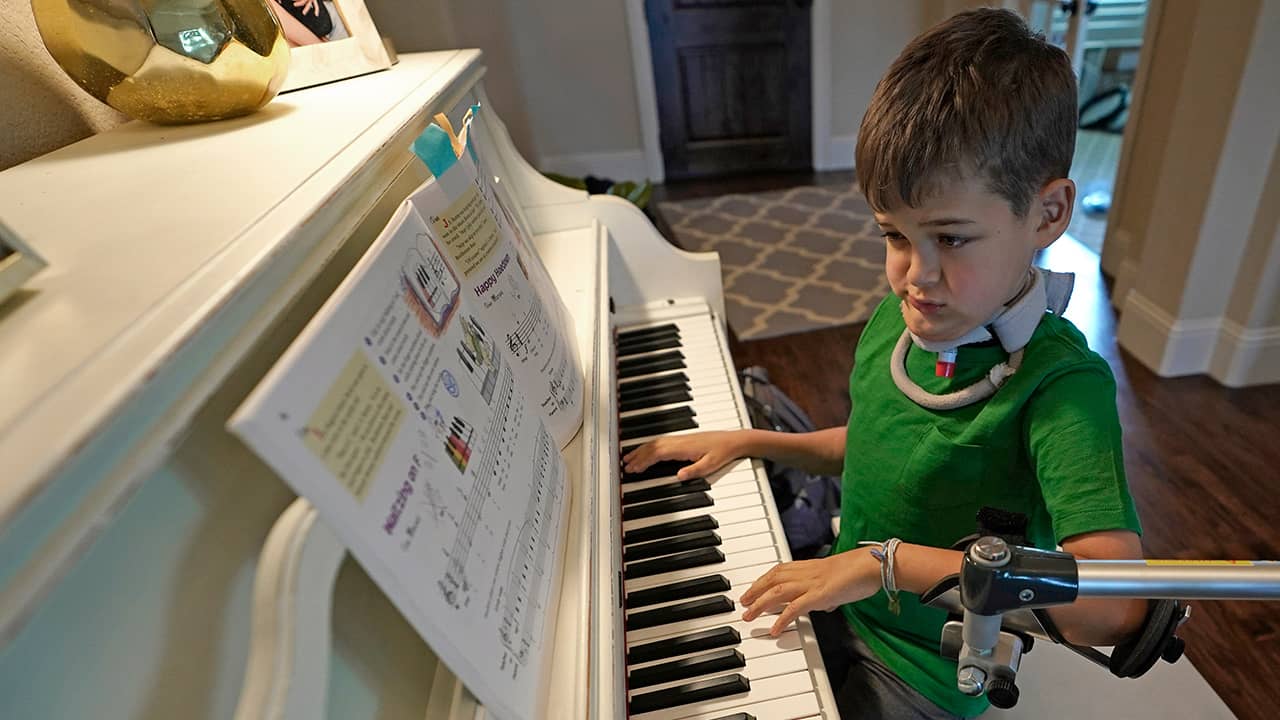

Experts Agree That Physical Therapy Makes a Difference
Scientists suspect the illness is being caused chiefly by a certain virus that was identified more than 55 years ago and may have mutated to become more dangerous. But they have yet to prove that.
And while doctors have deployed a number of treatments singly or in combination — steroids, antiviral medications, antibiotics, a blood-cleansing process — the CDC says there is no clear evidence they work.
Many parents say that when they first brought their child to the emergency room, they quickly realized to their horror that the doctors were at sea, too.
“Everyone is desperate for some magical thing,” said Rachel Scott, a Tomball, Texas, woman whose son Braden developed AFM in 2016 and has recovered somewhat after intensive physical therapy but still cannot move his right arm and has trouble swallowing and moving his neck.
A growing number of experts agree that physical therapy makes a difference.
“These kids can continue to recover very slowly, year over year. … It’s driven by how much therapy they do,” said Dr. Benjamin Greenberg of UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, one of the nation’s foremost experts on the condition.
Wilcox, Joey’s father, said his son made huge improvements that way. Joey can run and use his arms. Still, muscle tone is weak in his right leg and shoulder, and he still has left-side facial paralysis. “He can’t completely smile,” his dad said.
Experts Feel Certain the Main Culprit Is an Enterovirus Called EV-D68
Other stories are more tragic.
Katie Bustamante’s son Alex developed AFM in 2016. The suburban Sacramento, California, mother realized something was wrong when she asked the boy, then 5, why he wasn’t eating his yogurt. Alex replied that his thumb had stopped working and he couldn’t hold his spoon.
Government officials need to step up, Bustamante said.
“I want them to research it and find the cause, and I want them to find a way to prevent it,” she said. “This is growing. This shouldn’t be happening.”
More and more experts feel certain the main culprit is an enterovirus called EV-D68, based on the way waves of AFM have coincided with spikes of respiratory illnesses caused by EV-D68. Enteroviruses are a large family of viruses, some of which, such as polio, can damage the central nervous system, while many others cause mild symptoms or none at all.
In the U.S., doctors began reporting respiratory illnesses tied to EV-D68 in 1987, though usually no more than a dozen in any given year.
Then, in what may have been one of the first signs of the AFM waves to come, a 5-year-old boy in New Hampshire died in 2008 after developing neck tenderness and fever, then weakened arms and deadened legs. The boy had EV-D68, and in a report published in an obscure medical journal, researchers attributed his death to the virus.
The first real burst of AFM cases hit in 2014, when 120 were confirmed, with the largest concentrations in California and Colorado.

Just Four Cases Have Been Confirmed This Year so Far
What ensued was an even-year, odd-year pattern: Cases dropped to 22 in 2015, jumped to 149 in 2016, and fell again, to 35 in 2017. Last year they reached 228, a number that may grow because scores of illnesses are still being investigated.
CDC officials consider an illness AFM based on scans and other evidence showing a certain kind of damage to the spinal cord. Proof of an enterovirus infection is not required for a case to be counted, mainly because such evidence has been hard to come by. So far, CDC investigators have been able to find evidence of enteroviruses in the spinal fluid of only four of 558 confirmed cases.
Scientists are using more sensitive spinal-fluid tests in hopes of establishing the connection between AFM and EV-D68 more firmly. That, in turn, could spur more focused work on treatments and maybe even a vaccine.
Meanwhile, Fauci’s agency has put out a call for researchers to apply for federal funds, and is tapping a University of Alabama-anchored network of pediatric research centers to work on the illness.
The CDC is pledging a greater focus, too. Parents have accused the agency of doing little more than counting cases and have complained that when they tried to contact CDC, they encountered only automated phone trees and form responses.
CDC officials have begun holding meetings and calls with families, set up a scientific task force and working to monitor cases more closely.
Fauci suggested it would be a mistake to assume that surges will take place every other year forever. The next one “may be in 2019, for all we know,” he said.