Share
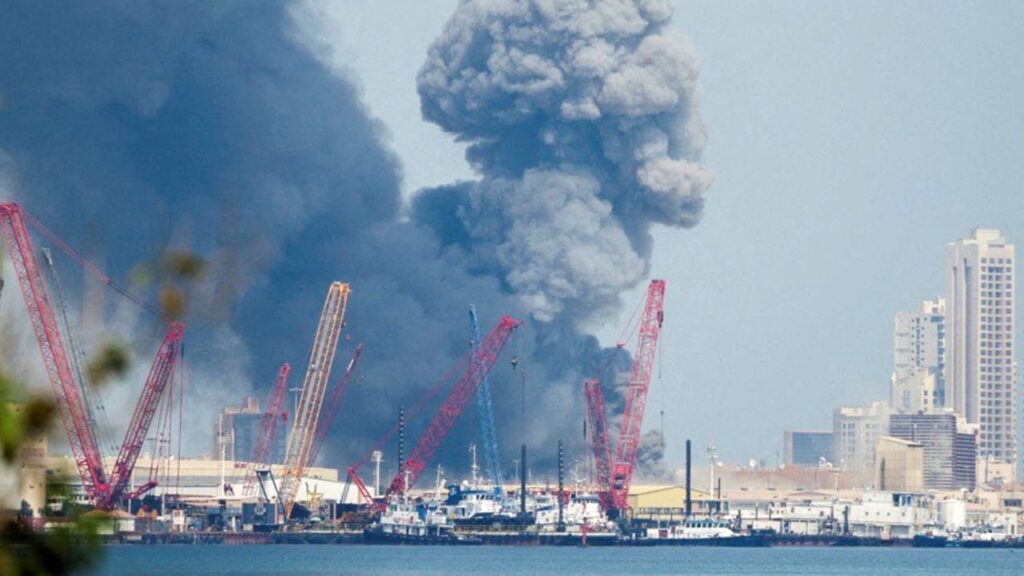
SONOMA — A county in Northern California wine country is exploring plans to sue a utility over a massive wildfire last fall that caused losses of $725 million when combined with rolling power shutoffs.
The supervisors also released findings of a report assessing the economic impact of the fire and four PG&E power shutoffs. The report by the Moody Analytics research company found the fire cost the county $620 million in losses and that the shutoffs caused an additional $105 million in losses.
“PG&E, not local taxpayers, should pay for costs and damages related to the fire, including harm to infrastructure, open space and disaster response costs,” county attorney Bruce Goldstein wrote in an email to the Press-Democrat of Santa Rosa.
Almost 195,000 residents, or 39% of the county’s population, was affected by the shutoffs between Oct 9 and Nov. 20, with the average resident disrupted for 2.5 days by any single outage, the report said.

The Ongoing Bankruptcy Case Shields PG&E From Other Lawsuits
The county’s action comes as PG&E tries to dig out of a financial hole created by a series of catastrophic fires from 2015 to 2018 that have been blamed on the utility’s electrical systems and managerial negligence. Faced with more than $50 billion in claims from fire victims, insurers and government agencies, PG&E has tried to rehabilitate itself in bankruptcy court for the past year. The company has settled most of those claims for a combined $25.5 billion.
The ongoing bankruptcy case shields PG&E from other lawsuits until the company emerges with a reorganization plan approved by the court and California regulators. PG&E needs to emerge from bankruptcy protection by June 30 to take advantage of a new state wildfire fund, meaning Sonoma County may have to wait until later this year before any lawsuit can proceed.
The cause of last fall’s fire is still under investigation. PG&E, however, has told state regulators that it had a problem at a transmission tower near the fire’s ignition point. The utility had shut off power to thousands of people in Northern California that day in a bid to prevent high winds from toppling power lines and igniting wildfires. Power was shut off to distribution lines but not to high-voltage transmission lines.
The county’s losses from the fire included damages to lands, parks, roads, and costs for emergency services, evacuations, debris removal, labor and watershed restoration, according to the board’s preliminary report.