Share
WASHINGTON — Scientists are dusting off some decades-old vaccines against other germs to see if they could provide a little stopgap protection against COVID-19 until a more precise shot arrives.
It may sound odd: Vaccines are designed to target a specific disease. But vaccines made using live strains of bacteria or viruses seem to boost the immune system’s first line of defense, a more general way to guard against germs. And history books show that sometimes translates into at least some cross-protection against other, completely different bugs.
There’s no evidence yet that the approach would rev up the immune system enough to matter against the new coronavirus. But given that a brand-new vaccine is expected to take 12 to 18 months, some researchers say it’s time to put this approach to a faster test, starting with a tuberculosis vaccine.
“This is still a hypothesis,” said Dr. Mihai Netea of Radboud University Medical Center in the Netherlands. But if it works, “it could be a very important tool to bridge this dangerous period until we have on the market a proper, specific vaccine.”
The World Health Organization issued a stern warning Monday not to use the TB vaccine against COVD-19, unless and until studies prove it works.
Already nearly 1,500 Dutch health care workers have rolled up their sleeves for one study that Netea’s team is leading. It uses that TB vaccine, named BCG, which is made of a live but weakened bacterial cousin of the TB germ.
Possibly Next in Line
In Australia, researchers hope to enroll 4,000 hospital workers to test BCG, too, and 700 already have received either the TB vaccine or a dummy shot. Similar research is being planned in other countries, including the U.S.
Possibly next in line: Oral polio vaccine, drops made of live but weakened polio viruses. The Baltimore-based Global Virus Network hopes to begin similar studies with that vaccine and is in talks with health authorities, network co-founder Dr. Robert Gallo told The Associated Press.
Rapid studies are needed to tell if there could be “long-ranging effects for any second wave of this,” said Gallo, who directs the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
At the U.S. National Institutes of Health, researchers are in early discussions about proposals to study the TB and polio vaccines as a possible COVID-19 defense, said agency spokeswoman Jennifer Routh.
There’s a big caution: Live vaccines are risky for people with weakened immune systems, and shouldn’t be tried against COVID-19 outside of a research trial, said Dr. Denise Faustman, immunobiology chief at Massachusetts General Hospital, who is planning a TB vaccine study.
“You can’t just roll it out,” she stressed. But, “it’s kind of an amazing opportunity to prove or disprove this off-target effect.”

The First Clues
Years ago, scientists began noticing with several live vaccines what Dr. Victor Nizet, an immune expert at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine, calls “an important curiosity that people have been interested in trying to harness.”
BCG is given mostly to newborns in developing countries, and it offers only partial protection against TB, a bacterial infection. But observational studies showed during childhood, the vaccinated tots had better overall survival, including from respiratory viruses.
In 2018, Netea’s team published a more direct test. They showed BCG stimulates initial immune defenses enough that it at least partly blocked another virus given experimentally a month later.
What about oral polio vaccine? Those clues emerged first from the former Soviet Union, said Konstantin Chumakov, a vaccine specialist at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, who stressed he was not speaking on behalf of the FDA. His mother was a Soviet scientist who in the 1970s published research showing flu cases dropped markedly after oral polio vaccination.
In 2015, Danish researchers also found some hints of cross-protection after oral polio vaccinations. The oral drops still are used in developing countries while the U.S. and other areas that have eliminated polio use the inactivated shot for routine childhood vaccines.
Different Kinds of Immunity
There are overlapping types of immune defenses. The usual goal of a vaccine is to prime the body to recognize a specific health threat and make antibodies able to fight back when that particular bug comes along.
But that takes time. So at the first sign of infection, a first line of foot soldiers — white blood cells — springs into action to fend off the invader in other ways, what’s called innate immunity. If they fail, then the body creates its more targeted special forces to join the fight.
BCG appears to be reprogramming innate immune cells so they can more readily eliminate the germ up front, said Netea, the Dutch researcher.
Scientists not involved in the effort to try these vaccines against COVID-19 say it’s worthwhile to test.
“The scientific rationale I think is quite logical,” said Nizet, the UC-San Diego immune specialist. “The unknown is whether coronaviruses are in the spectrum of things that are efficiently protected” by that first-line innate immunity.
Some scientists have theorized that countries with large BCG-vaccinated populations might fare better in the pandemic. But given problems with accurately counting the toll, it’s far too early to draw any conclusions, a caution the WHO reiterated Monday.
RELATED TOPICS:
Categories
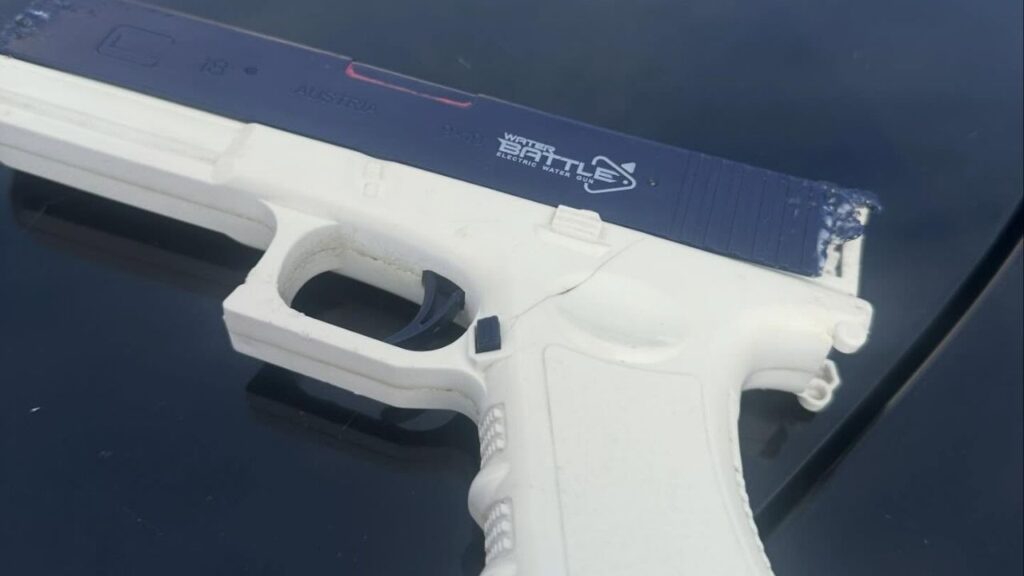

Teen Arrested at Visalia Mall After Firearm Report

Tumblr Goes Down for Thousands, Downdetector Reports