Share
Justin Silvera came off the fire lines in Northern California after a grueling 36 straight days battling wildfires and evacuating residents ahead of the flames. Before that, he and his crew had worked for 20 days, followed by a three-day break.
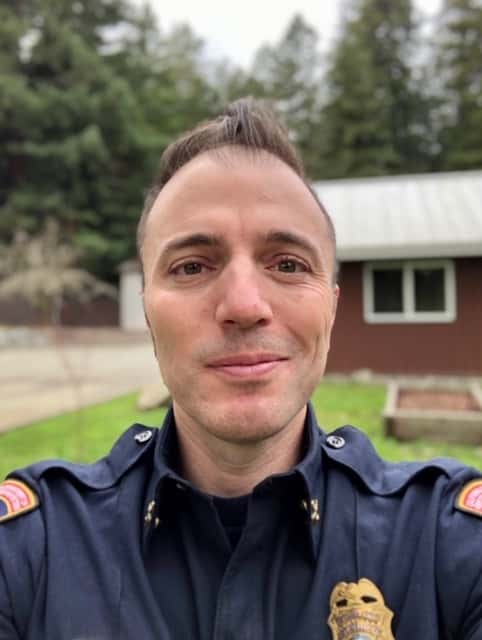

Silvera, a 43-year-old battalion chief with Cal Fire, California’s state firefighting agency, said he’s lost track of the blazes he’s fought this year. He and his crew have sometimes been on duty for 64 hours at a stretch, their only rest coming in 20-minute catnaps.
“I’ve been at this 23 years, and by far this is the worst I’ve seen,” Silvera said before bunking down at a motel for 24 hours. After working in Santa Cruz County, his next assignment was to head north to attack wildfires near the Oregon border.
His exhaustion reflects the situation up and down the West Coast fire lines: This year’s blazes have taxed the human, mechanical and financial resources of the nation’s wildfire fighting forces to an extraordinary degree. And half of the fire season is yet to come. Heat, drought and a strategic decision to attack the flames early combined with the coronavirus to put a historically heavy burden on fire teams.
“There’s never enough resources,” said Silvera, one of nearly 17,000 firefighters in California. “Typically with Cal Fire we’re able to attack — air tankers, choppers, dozers. We’re good at doing that. But these conditions in the field, the drought, the wind, this stuff is just taking off. We can’t contain one before another erupts.”
Washington State Forester George Geissler says there are hundreds of unfulfilled requests for help throughout the West. Agencies are constantly seeking firefighters, aircraft, engines and support personnel.
Fire crews have been summoned from at least nine states and other countries, including Canada and Israel. Hundreds of agreements for agencies to offer mutual assistance have been maxed out at the federal, state and local levels, he said.

Demand for Firefighting Resources Has Been High Since Mid-August
“We know that there’s really nothing left in the bucket,” Geissler said. “Our sister agencies to the south in California and Oregon are really struggling.”
Demand for firefighting resources has been high since mid-August, when fire officials bumped the national preparedness level to critical, meaning at least 80% of crews were already committed to fighting fires, and there were few personnel and little equipment to spare.
Because of the extreme fire behavior, “you can’t say for sure having more resources would make a difference,” said Carrie Bilbao, a spokesperson for the National Interagency Fire Center in Boise.
Andy Stahl, a forester who runs Forest Service Employees for Environmental Ethics, an advocacy group in Oregon, said it would have been impossible to stop some of the most destructive blazes, a task he compared to “dropping a bucket of water on an atomic bomb.”
But Stahl contends the damage could have been less if government agencies were not so keen to put out every blaze. By stamping out smaller fires and those that ignite during wetter months, Stahl said officials have allowed fuels to build up, setting the stage for bigger fires during times of drought and hot, windy weather.
That’s been exacerbated this year by the coronavirus pandemic, which prompted U.S. Forest Service Chief Vickie Christiansen to issue a directive in June to fight all fires aggressively, reversing a decades-long trend of allowing some to burn. The idea was to minimize large concentrations of firefighters by extinguishing blazes quickly.
Fighting the flames from the air was key to the strategy, with 35 air tankers and 200 helicopters being used, Forest Service spokesperson Kaari Carpenter said.
Ingalsbee Worried the Focus on Aggressively Attacking Every Fire Could Prove Lasting
Yet by Aug. 30, following the deaths of some firefighters, including four aviators, and several close calls, fire officials in Boise warned that long-term fatigue was setting in. They called for a “tactical pause” so fire commanders could reinforce safe practices.
Tim Ingalsbee, a member of the advocacy group Firefighters United for Safety, Ethics and Ecology, said the June directive from Christiansen returned the forest service to a mindset prevalent for much of the last century that focused on putting out fires as quickly as possible. He said allowing more fires to burn when they are not threatening life or property would free up firefighters for the most dangerous blazes.
With no end in sight to the pandemic, Ingalsbee worried the focus on aggressively attacking every fire could prove lasting.
“More crews, more air tankers, more engines and dozers still can’t overcome this powerful force of nature,” he said. “The crews are beat up and fatigued and spread thin, and we’re barely halfway through the traditional fire season.”
Cal Fire’s roughly 8,000 personnel have been fighting blazes from the Oregon border to the Mexico border, repeatedly bouncing from blaze to blaze, said Tim Edwards, president of the union for Cal Fire, the nation’s second largest firefighting agency.
“We’re battle-hardened, but it seems year after year, it gets tougher, and at some point in time we won’t be able to cope. We’ll reach a breaking point,” said Edwards, a 25-year veteran.
The immediate dangers of the fires are compounded by worries about COVID in camp and at home.

California Alone Has Spent $529 Million Since July 1 on Wildfires
Firefighters “see all this destruction and the fatigue, and then they’re getting those calls from home, where their families are dealing with school and child care because of COVID. It’s stressing them out, and we have to keep their heads in the game,” he said.
COVID also has limited the state’s use of inmate fire crews — either because of early inmate releases to prevent outbreaks in prisons or because many are under quarantine in those prisons, both Berland and Geissler said.
Aside from the human toll, the conflagrations in Colorado and Utah, New Mexico and Arizona, and now California and the Pacific Northwest have cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
California alone has spent $529 million since July 1 on wildfires, said Daniel Berlant, assistant deputy director of Cal Fire. By comparison, the state spent $691 million the entire fiscal year that ended June 30. The U.S. government will reimburse most state costs for the biggest disasters.
Back in the field, Silvera and his crew saved two people at the beginning of their 26-day duty tour. The two hikers encountered the crew after the firefighters themselves were briefly trapped while trying to save the headquarters building at Big Basin Redwoods State Park.
“We got in a bad spot, and there were a few hours there we didn’t know if we’d make it,” Silvera said. “Those people found us, and we wouldn’t have been in there.”
“That’s what you sign up for.”
RELATED TOPICS:
Categories