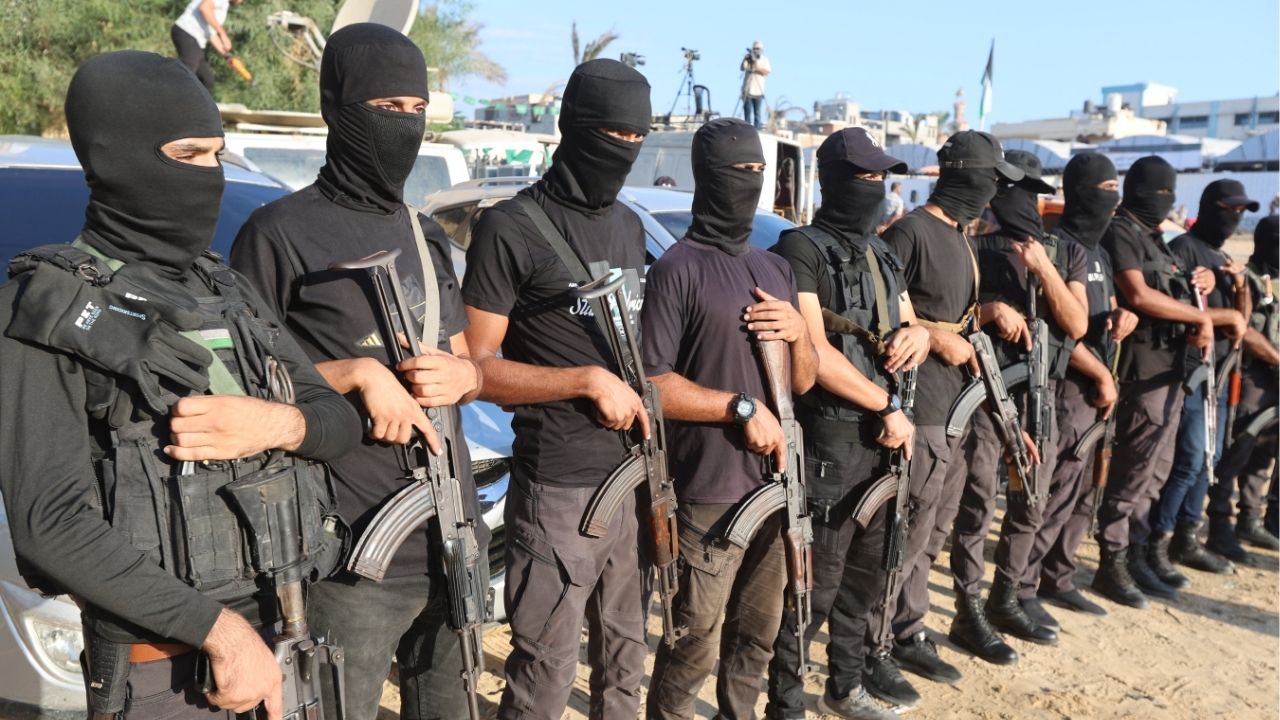
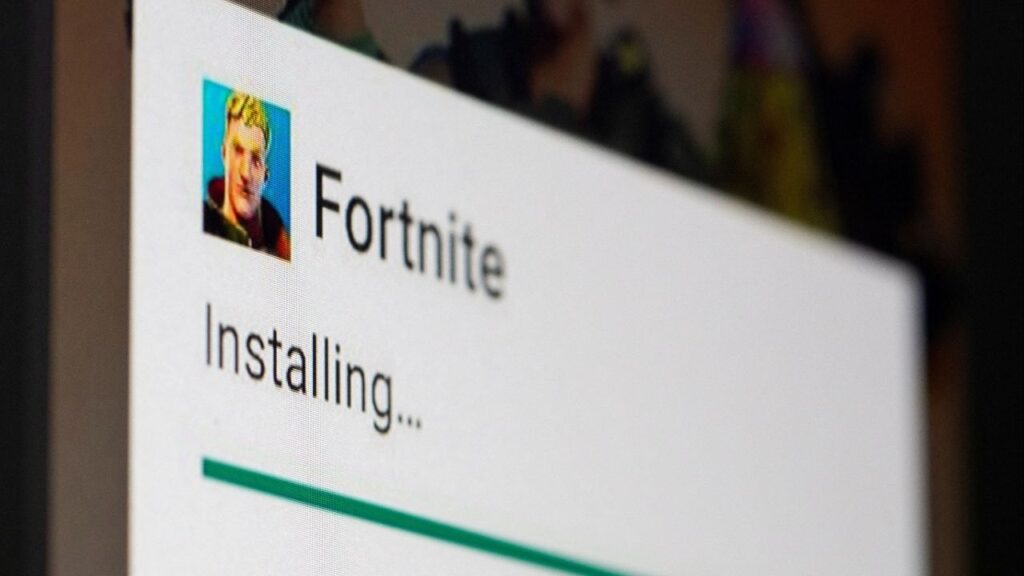
Palestinian militants stand guard on the day that hostages held in Gaza since the deadly October 7, 2023 attack, are handed over to the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), as part of a ceasefire and hostages-prisoners swap deal between Hamas and Israel, in Khan Younis, southern Gaza Strip, October 13, 2025. (Reuters/Ramadan Abed)

- Hamas reasserted control in Gaza after the ceasefire, killing 33 rivals as Trump signaled temporary policing approval.
- Armed Hamas fighters returned to Gaza’s streets, underscoring the challenge to U.S. plans for a demilitarized, internationally supervised enclave.
- Internal clan clashes highlight the fragile postwar security landscape, with Israel-linked rivals posing threats to Hamas’ authority.
Share
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
CAIRO — A greatly weakened Hamas has sought to reassert itself in Gaza since a ceasefire took hold, killing at least 33 people in a crackdown on groups that have tested its grip and appearing to get a U.S. nod to temporarily police the shattered enclave.
Pummeled by Israel during the war ignited by the October 7, 2023 attacks, Hamas has gradually sent its men back into the streets of Gaza since the ceasefire began on Friday, moving cautiously in case it suddenly collapses, according to two security sources in the territory.
On Monday, Hamas deployed members of its Qassam Brigades military wing as it freed the last living hostages seized from Israel two years ago. It was a reminder of one of the major challenges facing U.S. President Donald Trump’s effort to secure a lasting deal for Gaza, as the U.S., Israel and many other nations demand Hamas disarm.
Reuters footage showed dozens of Hamas fighters lined up at a hospital in southern Gaza, one wearing a shoulder patch identifying him as a member of the elite “Shadow Unit” that Hamas sources say was tasked with guarding hostages.
One of the Gaza sources, a security official, said that since the ceasefire, Hamas forces had killed 32 members of “a gang affiliated with a family in Gaza City”, while six of its personnel had also been killed.
Later on Monday, a video circulating on social media appeared to show several masked gunmen, some of them wearing green headbands resembling ones worn by Hamas, shooting with machine guns at least seven men after forcing them to kneel in the street. Posts identified the video as filmed in Gaza on Monday. Civilian spectators cheered “Allah Akbar,” or God is Great, and called those killed “collaborators.”
Reuters could not immediately verify the events of the video, its date or location. There was no immediate response from Hamas.
Last month, Hamas-led authorities said they executed three men accused of collaborating with Israel. The video of the public killing was shared on social media.
Temporary Policing Role?
Trump’s plan foresees Hamas out of power in a demilitarize Gaza run by a Palestinian committee under international supervision. It calls for the deployment of an international stabilization mission that will train and support a Palestinian police force.
But Trump, speaking on his way to the Middle East, suggested Hamas had been given a temporary green light to police Gaza.
“They do want to stop the problems, and they’ve been open about it, and we gave them approval for a period of time,” he said, responding to a journalist’s question about reports that Hamas was shooting rivals and instituting itself as a police force.
After the ceasefire took effect, Ismail Al-Thawabta, head of Hamas’ Gaza government media office, told Reuters the group would not allow a security vacuum and that it would maintain public safety and property.
Hamas has ruled out any discussion of its arsenal, saying it would be ready to surrender its arms to a future Palestinian state. The group has said it seeks no role in Gaza’s future governing body, but that this should be agreed upon by Palestinians with no foreign control.
Internal Conflict With Clans
As the war dragged on, a diminished Hamas faced growing internal challenges to its control of Gaza from groups with which it has long been at odds, often affiliated with clans.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said earlier this year that Israel had been arming clans that oppose Hamas, without identifying them.
In Gaza City, Hamas has mostly battled the Doghmosh clan, residents and Hamas sources said.
The security official did not identify the “gang” who had been targeted in Gaza City, nor say whether it had been suspected of receiving support from Israel.
The most prominent anti-Hamas clan leader is Yasser Abu Shabab, who is based in the Rafah area – an area from which Israel has yet to withdraw.
Offering attractive salaries, his group has recruited hundreds of fighters, a source close to Abu Shabab told Reuters earlier this year. Hamas calls him a collaborator with Israel, which he denies.
The Gaza security official said that separately to the clashes in Gaza City, Hamas security forces had killed Abu Shabab’s “right-hand man” and efforts were underway to kill Abu Shabab himself.
Abu Shabab did not immediately respond to questions on the official’s comments. Reuters could not immediately verify the claim that his aide had been killed.
Hussam al-Astal, another anti-Hamas figure based in Khan Younis in areas controlled by Israel, taunted the group in a video message on Sunday, saying that once it hands over the hostages, its role and rule in Gaza would be over.
Palestinian analyst Reham Owda said Hamas actions aimed to deter groups that had collaborated with Israel and contributed to insecurity during the war. Hamas also aimed to show that its security officers should be part of a new government, though this would be rejected by Israel, she said.
—
(Reporting by Nidal al-Mughrabi; Writing by Tom Perry; Editing by Ros Russell, Aidan Lewis and Rosalba O’Brien)